Diabetes is a condition that affects how the body uses blood sugar (glucose), a primary source of energy for cells. The body’s ability to manage blood sugar depends on a hormone called insulin. In diabetes, the body either stops making insulin or doesn’t use it well, causing blood sugar levels to rise. When not managed, high blood sugar can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, and nerve damage.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: This type usually starts in children or young adults and is less common than Type 2. In Type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks the cells that make insulin, meaning no insulin is produced. People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin daily to survive.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common type, Type 2 diabetes generally develops in adults, although it’s increasingly seen in children and teens. In Type 2 diabetes, the body produces some insulin, but it isn’t enough or doesn’t work well. It can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medications, although some people may also need insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy. It usually goes away after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later. Both mother and child should be monitored for diabetes risk in the future.
- Prediabetes: Prediabetes means blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It’s a warning sign for Type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes can often prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Several factors increase the risk of diabetes:
- Family History: Having close relatives with diabetes raises the risk.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese, especially with excess belly fat, significantly increases the risk.
- Age: The risk of Type 2 diabetes rises with age, particularly after age 45.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Ethnicity: Some ethnicities, including African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian American, are at higher risk.
- High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: These increase the chances of developing diabetes and complications.
- Conditions such as PCOS: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk of diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: If a woman had gestational diabetes during pregnancy, her risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later increases.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Fatigue or feeling very tired
- Blurred vision
- Numbness or tingling in hands or feet
- Slow-healing cuts and bruises
- Unintended weight loss (mainly in Type 1 diabetes)
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider to assess your blood sugar levels.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes
Taking steps toward a healthier lifestyle can help prevent Type 2 diabetes or delay its onset. Here are some effective ways to lower the risk:
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit sugary drinks, processed foods, and refined carbohydrates that can raise blood sugar quickly.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently. Aim for at least 150 minutes a week of moderate activity, like walking, or 75 minutes of vigorous activity, like jogging.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing even a small amount of weight can reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes, especially if you carry extra weight around the abdomen.
- Get Regular Health Check-ups: Regular blood sugar screenings can help detect prediabetes early, giving you the chance to make changes before diabetes develops.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase insulin resistance and raise blood sugar levels. Quitting can help reduce the risk of diabetes and improve overall health.
Managing Diabetes
Managing diabetes involves lifestyle changes and sometimes medications to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range. The main areas of focus are:
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: Keeping track of blood sugar levels helps people with diabetes make necessary adjustments to diet, exercise, or medications.
- Healthy Eating: Following a diabetes-friendly diet, including foods high in fiber and low in added sugars, is essential to manage blood sugar.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, which can improve blood sugar control.
- Medication: Some people need medications or insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Understanding Complications of Diabetes
Without proper management, diabetes can cause serious complications:
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Diabetes raises the risk of heart disease and stroke. High blood sugar damages blood vessels and can lead to heart-related issues.
- Kidney Disease: The kidneys filter waste from the blood, but high blood sugar can damage the filtering system, leading to kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Vision Loss: Diabetes can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to diabetic retinopathy, which can cause vision loss or blindness.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Nerve damage from high blood sugar levels can lead to pain, numbness, and even infections, especially in the feet.
- Foot Damage: Nerve damage and poor blood flow in the feet can lead to infections, ulcers, and even amputations if not treated early.
By following a healthy lifestyle, regularly monitoring blood sugar, and having routine check-ups, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of complications and maintain a high quality of life.
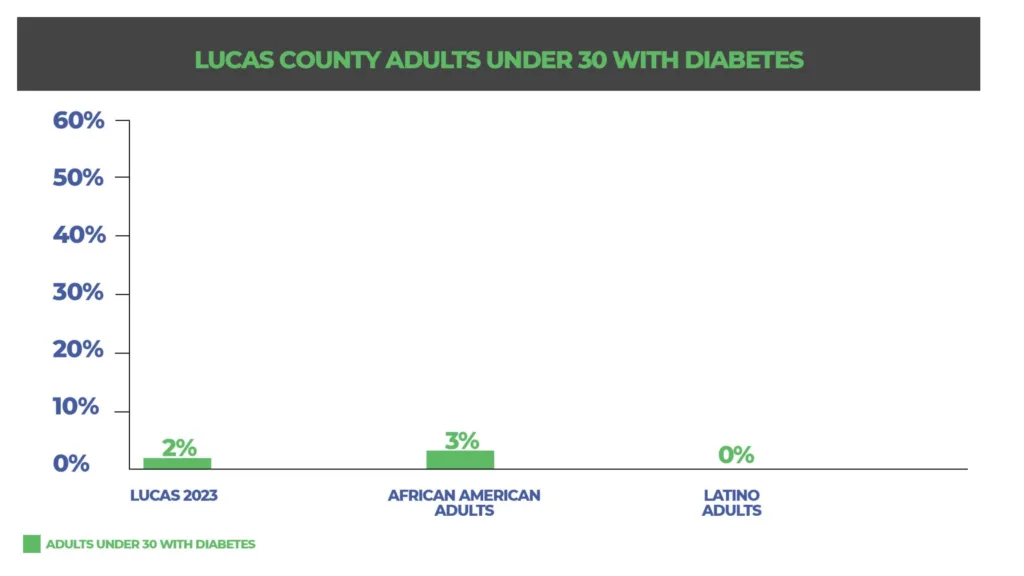
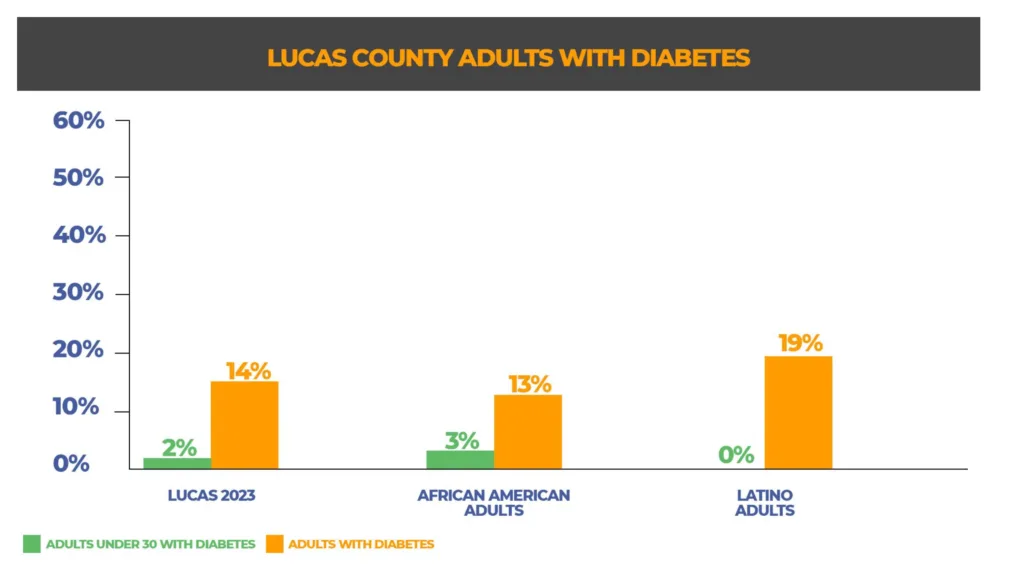
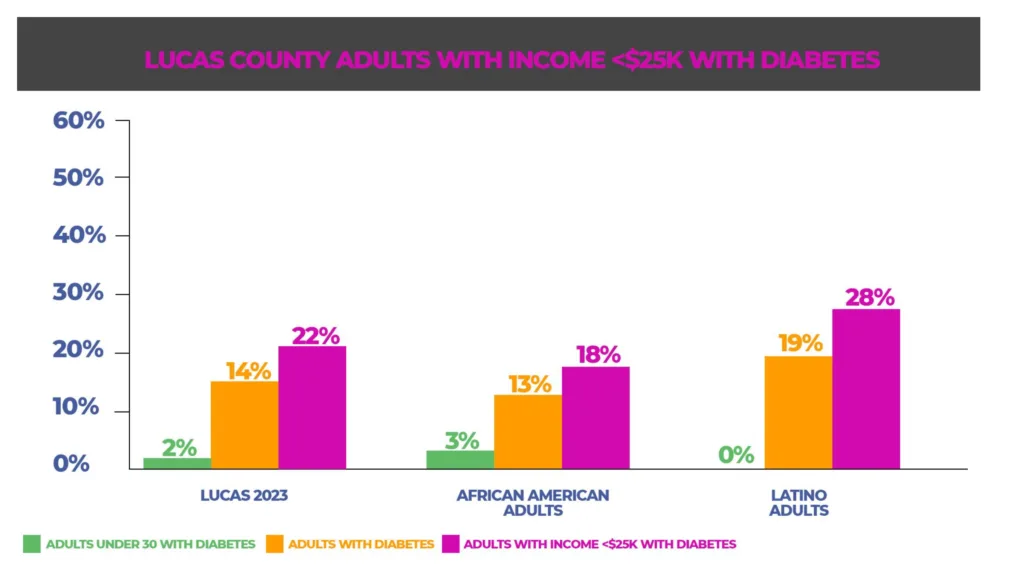
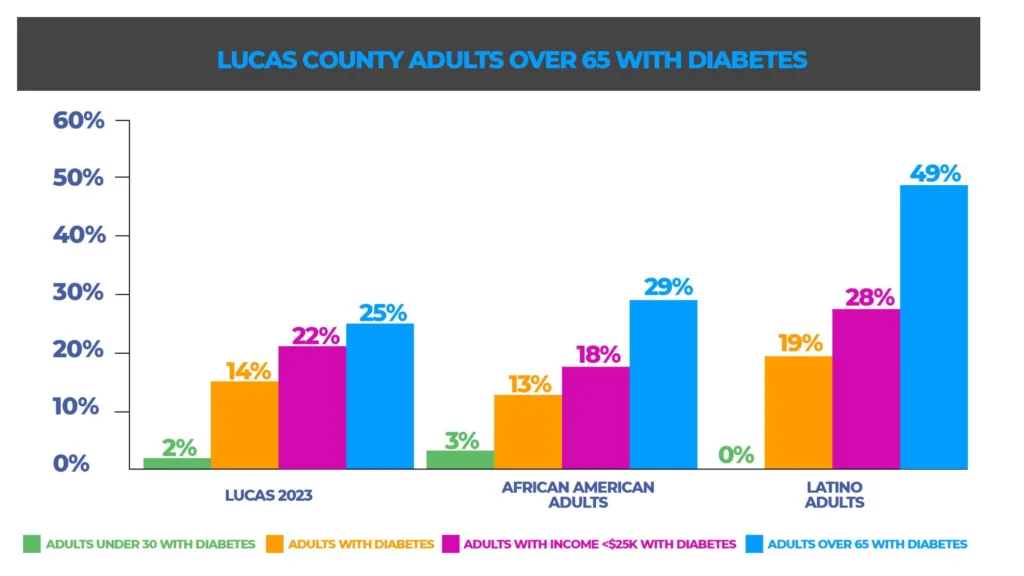
Diabetes in Lucas County